所用技术栈:Next.js, Tailwind CSS, TypeScript, DaisyUI
Link
使用 anchor 标签这种导航方式会重新加载重复网页文件的,而不是替换需要的内容:
export default function Home() {
return (
<main>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<a href='/users'>Users</a>
</main>
);
}因此使用 next 中的Link组件:
<Link href='/users'>Users</Link>CSR & SSR
-
用户端可交互,暴露密钥给用户,标准 React App 的工作方式
-
服务端资源占用小,搜索引擎 bot 可以查看页面并建立索引,在服务器上保留 API 等敏感数据,失去了交互性
因此现实中默认使用服务端组件(Next 中就是),必须使才使用客户端组件。
比如在一个商城应用中,应该把导航、侧边栏、页码页脚等组件放在服务端,对于需要交互的商品组件,可以只把需要点击的微小组件(如“AddToCart”)发送到客户端,
Data Fetching
fetch
- Client:
useState(),useEffect()ReactQuery
Large bundles, No SEO(Search Engine Optimization), Less secure, Extra roundtrip to server
- Server:
Typescript Magic:
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
const UsersPage = async () => {
const res = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users');
const users: User[] = await res.json();
return (
<>
<h1>Users</h1>
<ul>
{users.map((users) => (
<li key={users.id}>{users.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</>
);
};Caching
(-> slower)
Memory -> File System -> Networks
For this reason, Next.js has a built in data cache( in fetch ):
const res = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users', {
cache: 'no-store',
});
// or
{
next: {
revalidate: 10;
}
} // 10sRendering
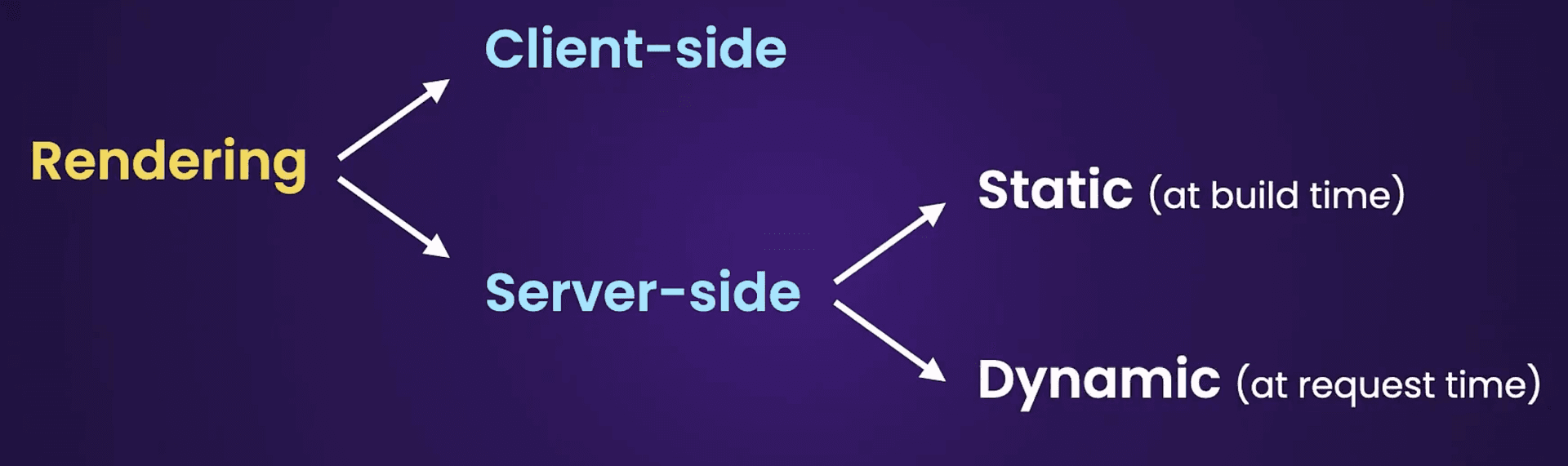
对于
<p>{new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}</p>npm run build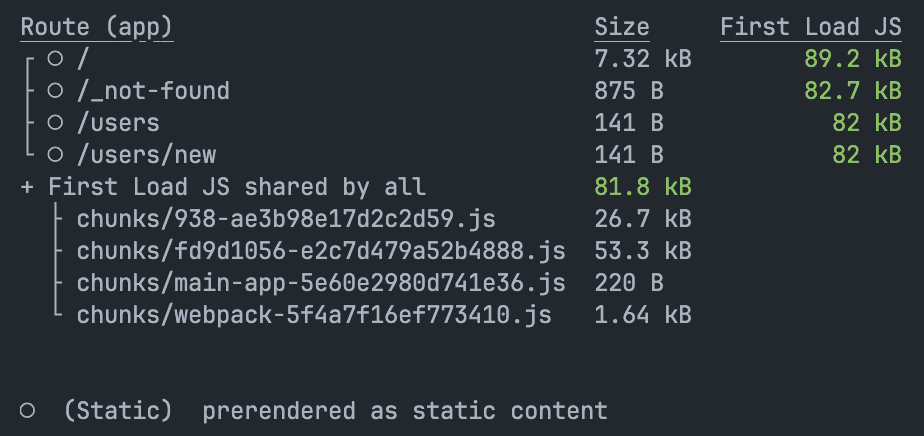
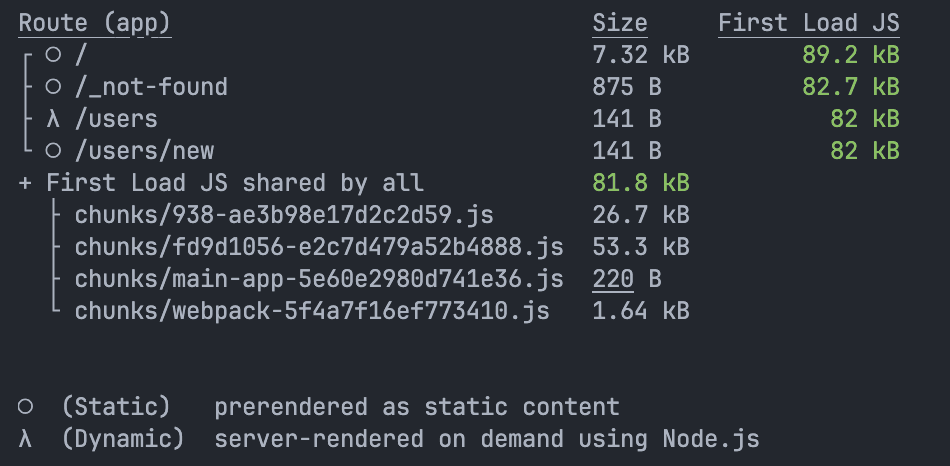
使用cache: 'no-store'后:
Tailwind CSS
CSS Module
scoped to a single component / page, preventing clashing and overwriting
新建ProductCard.module.css,使用:
import styles from './ProductCard.module.css'
<div className={styles.card}>Nextjs 使用 postcss 来生成唯一类名。
Tailwind
<div className='p-5 my-5 bg-sky-400 text-white text-xl hover:bg-sky-600'>好神奇,删除这个组件就是删除了,不需要再去找对应的 css 文件。
daisyUI
类似 boostrap。
- Installation
npm i -D daisyui@latest- Then add daisyUI to the
tailwind.config.tsfiles:
module.exports = {
//...
plugins: [require('daisyui')],
};button
button className='btn btn-primary' onClick={() => console.log('clicked')}>Add to cart</button>theme
tailwind.config.ts:
plugins: [require("daisyui")],
daisyui: {
themes: ["winter"],
},layout.tsx:
<html lang="en" data-theme="winter">Routing
-
page.tsx:可公开访问的页面文件 -
layout.tsx:定义页面通用布局 -
loading.tsx:显示加载的 UI ^bbaedd -
route.tsx:创建 API -
not-found.tsx:显示常规错误 -
error.tsx:自定义错误页面Dynamic Route
动态路由就是带参数的路由:
- 在
[id]文件夹的page.tsx中:
interface Props {
parmas: { id: number };
}
// 这里是直接解构出参数变量
const UserDetailPage = ({ parmas: { id } }: Props) => {
return <div>UserDetailPage {id}</div>;
};- 更多参数的路由
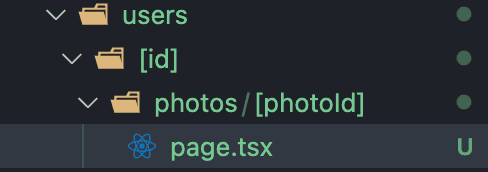
interface Props {
params: { id: number; photoId: number };
}
const PhotoPage = ({ params: { id, photoId } }: Props) => {
return (
<div>
PhotoPage {id} {photoId}
</div>
);
};Catch-all Segments
文件名:[[...slug]] 使所有路径 segments 的捕获变为可选项,即还可以匹配所在主路径本身:
interface Props {
params: { slug: string[] };
}
const ProductPage = ({ params: { slug } }: Props) => {
return <div>ProductPage {slug}</div>;
};Accessing Query String Parameter
page.tsx中将路由字符传入组件中:
interface Props {
searchParams: { sortOrder: string };
}
const UsersPage = async ({ searchParams: { sortOrder } }: Props) => {
return (
<>
<h1>Users</h1>
<UserTable sortOrder={sortOrder} />
</>
);
};UserTable.tsx中:
import { sort } from 'fast-sort';
interface Props {
sortOrder: string;
}
const UserTable = async ({ sortOrder }: Props) => {
const res = await fetch(
'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users',
{cache: 'no-store'});
const users: User[] = await res.json();
const sortedUsers = sort(users).asc(
sortOrder == 'email'
? user => user.email
: user => user.name
);
return (...
<Link href="/users?sortOrder=name">Name</Link>
</th>
<th>
<Link href="/users?sortOrder=email">Email</Link>
...
{sortedUsers.map(users => <tr key={users.id}>
<td>{users.name}</td>
<td>{users.email}</td></tr>)}...
}Layout
使用 layout 来创建在多个页面中共享的 UI
- 在新建的 admin 文件夹中
layout.tsx,可以定义这个文件夹中page.tsx的布局:
import React, { ReactNode } from 'react';
interface Props {
children: ReactNode;
}
const AdminLayout = ({ children }: Props) => {
return (
<div className='flex'>
<aside className='mr-5 bg-slate-200 p-5'>Admin Sidebar</aside>
<div>{children}</div>
</div>
);
};
export default AdminLayout;define global NavBar
- app 文件夹中
NavBar.tsx:
import Link from 'next/link';
import React from 'react';
const NavBar = () => {
return (
<div className='flex bg-slate-200 p-5'>
<Link href='/' className='mr-5'>
Next.js
</Link>
<Link href='/users'>Users</Link>
</div>
);
};
export default NavBar;layout.tsx:
return (
<html lang="en" data-theme="winter">
<body className={inter.className}>
<NavBar />
<main className='p-5 '>
{children}
</main>
</body>
</html>overwrite base layer style
in global.css:
@layer base {
h1 {
@apply mb-3 text-2xl font-bold;
}
}Navigation
Link
- 只下载目标页面内容
- 预获取 viewport 内链接的页面
- 将页面缓存在客户端中
Porgrammatic Navigation
注意这里,默认的 import 路径可能不是这个:
'use client';
import { useRouter } from 'next/navigation';
import React from 'react';
const NewUserPage = () => {
const router = useRouter();
return (
<button className='btn' onClick={() => router.push('/users')}>
Create
</button>
);
};Show Loading UIs
通过流式传输(streaming),客户端初始接受的 html 文件后续生命周期中会接受 loading 后的内容,不影响 SEO:
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading...</p>}>
<UserTable sortOrder={sortOrder} />
</Suspense>多页面 loading:
- 在全局
layout.css中:
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading...</p>}>{children}</Suspense>- 通过loading files(
loading.tsx):
const Loading = () => {
return <span className='loading loading-spinner loading-md'></span>;
};例子中是 DaisyUI 的组件。
Errors
Not Found Errors
在想要实现的文件目录下编辑not-found.tsx,如:
import { notFound } from 'next/navigation'
const UserDetailPage = ({ params: {id} }: Props) => {
if (id > 10) notFound()Unexpected Errors
生产环境下,报错的页面可以自定义error.tsx:
'use client';
import React from 'react';
interface Props {
error: Error;
reset: () => void;
}
const ErrorPage = ({ error, reset }: Props) => {
console.log('error', error);
return (
<>
<div>An Unexpected Error has Occured</div>
<button className='btn' onClick={() => reset()}>
Retry
</button>
</>
);
};global-error.tsx可以捕获全局 layout 中的错误。
Building APIs
Route Handler in app/api/users/route.tsx:
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from 'next/server';
export function GET(request: NextRequest) {
return NextResponse.json([
{ id: 1, name: 'Mosh' },
{ id: 2, name: 'John' },
]);
}- Get a single object
interface Props {
params: { id: number };
}
export function GET(request: NextRequest, { params }: Props) {}
// or
export function GET(
request: NextRequest,
{ params }: { params: { id: number } }
) {}in api/users/[id]:
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from 'next/server';
export function GET(
request: NextRequest,
{ params }: { params: { id: number } }
) {
if (params.id > 10)
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'User Not Found!' }, { status: 404 });
return NextResponse.json({ id: 1, name: 'mosh' });
}- Creating Object
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from 'next/server';
export function GET(request: NextRequest) {
return NextResponse.json([
{ id: 1, name: 'Mosh' },
{ id: 2, name: 'John' },
]);
}
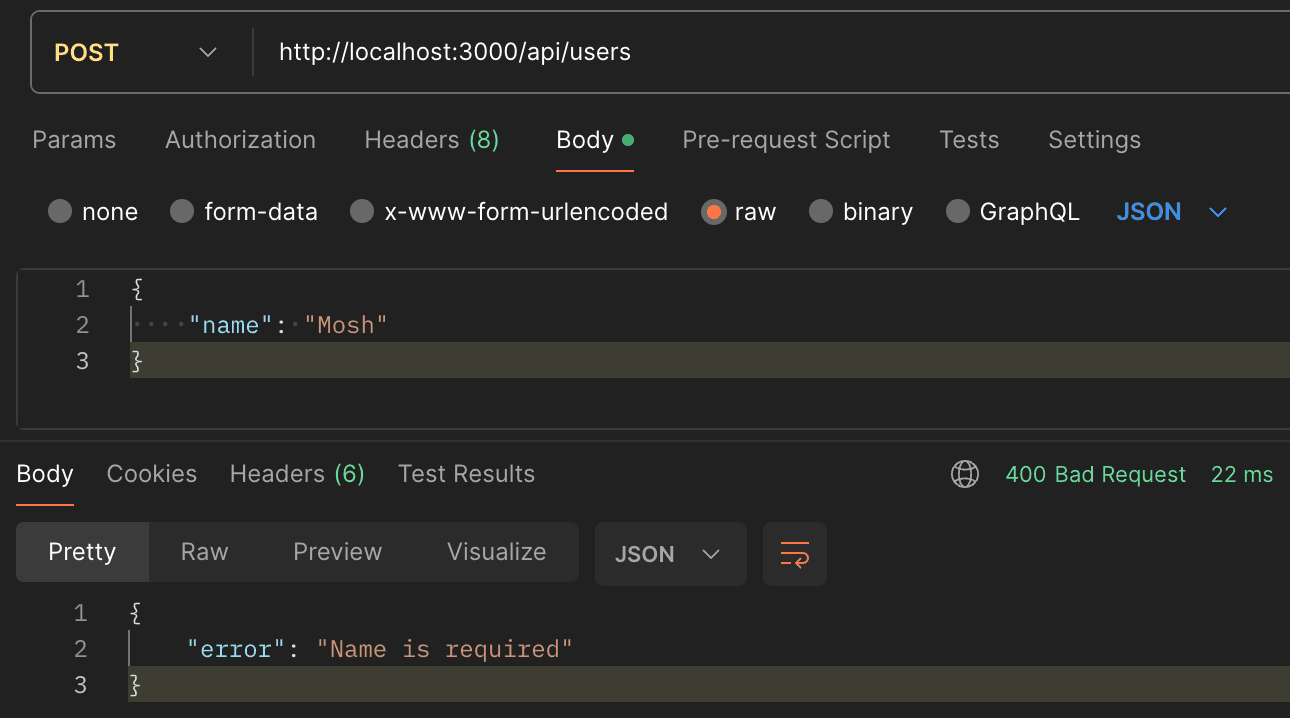
export async function POST(request: NextRequest) {
const body = await request.json();
// if invalid, return 400
if (!body.name)
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'Name is required' }, { status: 400 });
return NextResponse.json({ id: 1, name: body.name }, { status: 201 });
}
- Update an Object
// PUT for replacing object, PATCH for updating 1 or more properties
export async function PUT(
request: NextRequest,
{ params }: { params: { id: number } }
) {
// Validate the request body
const body = await request.json();
if (!body.name)
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'Name is required' }, { status: 400 });
if (params.id > 10)
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'User Not Found!' }, { status: 404 });
return NextResponse.json({ id: 1, name: body.name });
}- Delete an Object
export function DELETE(
request: NextRequest,
{ params }: { params: { id: number } }
) {
if (params.id > 10)
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'User Not Found!' }, { status: 404 });
return NextResponse.json({});
}Validating Request with Zod
对于复杂的 object,if-else 显然不再方便使用,最好使用 validation library,如zod
api/users/schema.ts:
import { z } from 'zod';
const schema = z.object({
name: z.string().min(3),
// email: z.string().email(),
// age: z.number()
});
export default schema;api/users/[id]/route.tsx:
export async function POST(request: NextRequest) {
const body = await request.json();
const validation = schema.safeParse(body);
// if invalid, return 400
if (!validation.success)
return NextResponse.json(validation.error.errors, { status: 400 });
return NextResponse.json({ id: 1, name: body.name }, { status: 201 });
}